

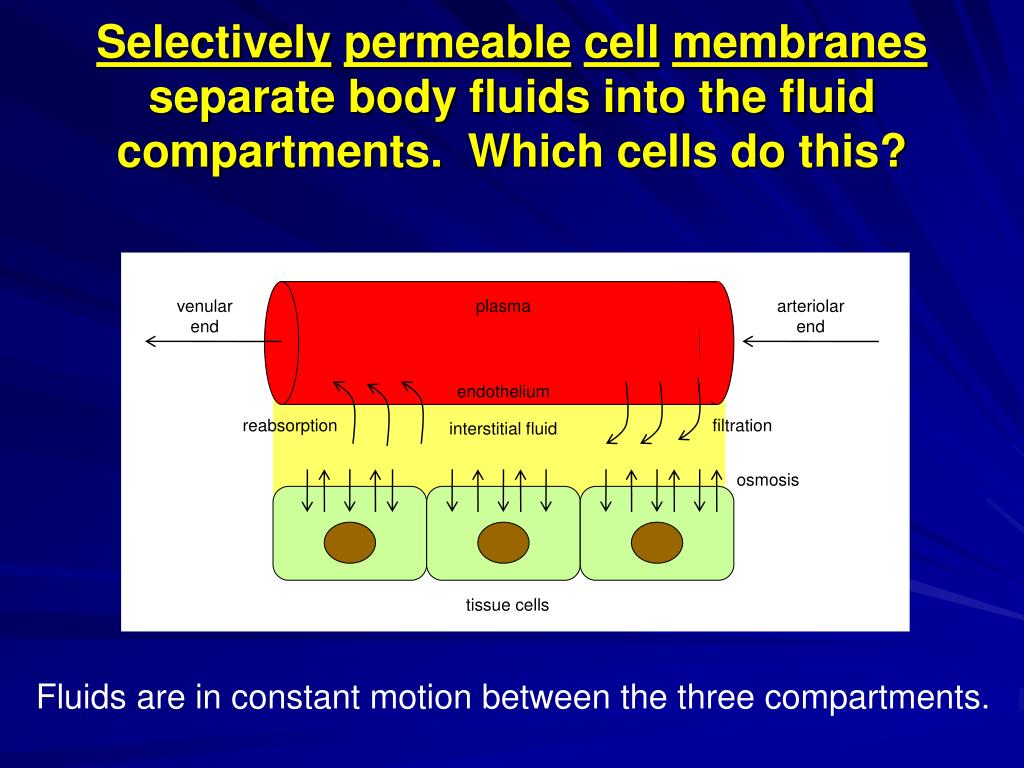
When blood volume decreases due to sweating, from what source is water taken in by the blood? Watch this video to learn more about body fluids, fluid compartments, and electrolytes. Because these fluids are outside of cells, these fluids are also considered components of the ECF compartment. These include the cerebrospinal fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord, lymph, the synovial fluid in joints, the pleural fluid in the pleural cavities, the pericardial fluid in the cardiac sac, the peritoneal fluid in the peritoneal cavity, and the aqueous humor of the eye. Cells are separated from the IF by a selectively permeable cell membrane that helps regulate the passage of materials between the IF and the interior of the cell. Gases, nutrients, and waste materials travel between capillaries and cells through the IF. Plasma travels through the body in blood vessels and transports a range of materials, including blood cells, proteins (including clotting factors and antibodies), electrolytes, nutrients, gases, and wastes. Approximately 20 percent of the ECF is found in plasma. The ECF accounts for the other one-third of the body’s water content. An appropriate balance of solutes inside and outside of cells must be maintained to ensure normal function. As a result, water will move into and out of cells and tissues, depending on the relative concentrations of the water and solutes found there. Osmosis is basically the diffusion of water from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration, along an osmotic gradient across a semi-permeable membrane. In the body, water moves through semi-permeable membranes of cells and from one compartment of the body to another by a process called osmosis.
For instance, sodium ions (Na +) and chloride ions (Cl –) are often referred to as electrolytes. Often in medicine, a mineral dissociated from a salt that carries an electrical charge (an ion) is called and electrolyte. In the human body, solutes vary in different parts of the body, but may include proteins-including those that transport lipids, carbohydrates, and, very importantly, electrolytes. The dissolved substances in a solution are called solutes. The chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions.
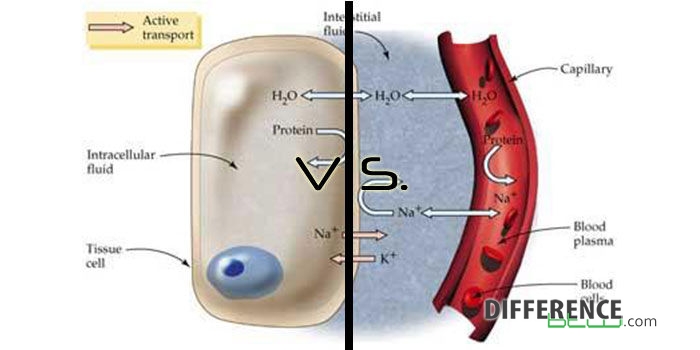

Contrast the composition of the intracellular fluid with that of the extracellular fluid.Explain the importance of water in the body.\)īy the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
